

In the world of chemical production, methanol has emerged as a versatile and valuable feedstock. Thanks to advanced catalytic processes, methanol can be transformed into key hydrocarbons—most notably olefins like ethylene and propylene, which are essential building blocks for plastics, fibers, and resins. Two of the most important processes enabling this conversion are Methanol-to-Olefins (MTO) and Methanol-to-Propylene (MTP). While they sound similar, they serve different roles in the industry. Understanding the difference between MTO and MTP catalysts can help you select the right technology for your project.
What is MTO?
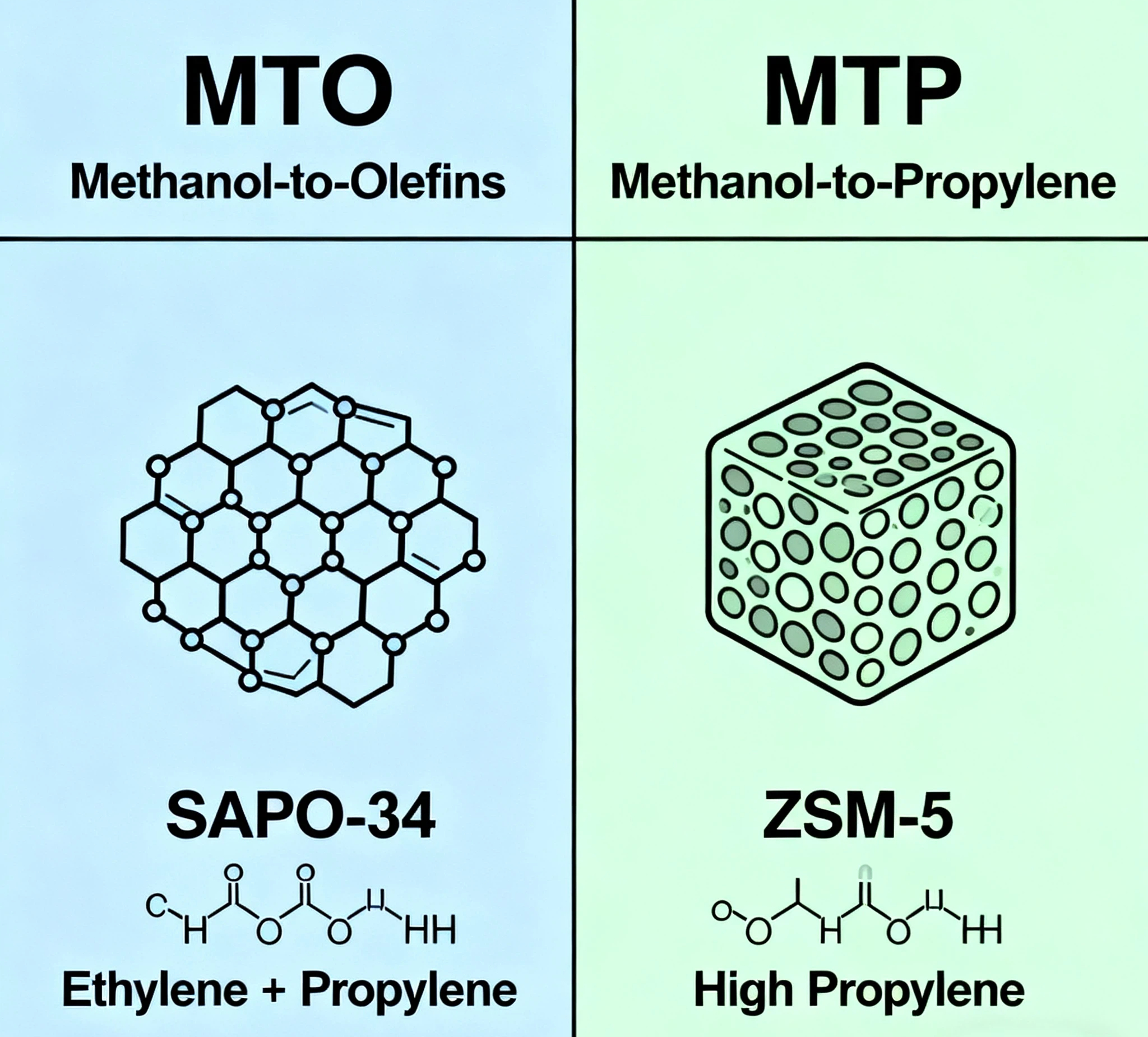
MTO, or Methanol-to-Olefins, is a catalytic process that converts methanol
primarily into ethylene and propylene. These light olefins are in high demand
for producing polyethylene and polypropylene. The MTO reaction typically uses a
class of catalysts known as zeolites—often SAPO-34—which have a unique porous
structure that favors the formation of smaller olefin molecules. Because of its
flexibility, MTO is ideal when both ethylene and propylene are target products,
allowing producers to adjust output based on market needs.
What is MTP?
MTP, or Methanol-to-Propylene, is a more specialized process designed to
maximize the yield of propylene. While MTO gives a balanced mix of ethylene and
propylene, MTP uses different types of zeolite catalysts, such as ZSM-5, which
are tuned to promote reactions that lead to higher propylene selectivity. This
makes MTP especially valuable in regions where propylene demand outstrips
supply, offering a reliable pathway from methanol to one of the most widely
used petrochemicals.
Key Differences Between MTO and MTP
Catalysts
The main distinction lies in the catalyst composition and resulting product
slate:
How to Choose Between MTO and MTP
Catalysts
Your choice depends largely on your target market and product goals. If you
need both ethylene and propylene, MTO offers flexibility. If your focus is
specifically on maximizing propylene production—for example, in polypropylene
manufacturing—MTP is likely the better option. Other factors include methanol
supply, plant location, and catalyst lifetime, which can impact overall
economics.